Plasmatherapies
The term plasmapheresis encompass different techniques (filtration or adsorption on plasma), which remove not all but only specific elements contained in the plasma, and altogether allow to treat a large number of diseases.
TPE
Therapeutic Plasma Exchange
in case of
Auto-immune diseases
Rejection of transplanted organs
Intoxication
TPE is usually performed with 5-10 consecutive sessions of 1-2 hours.
TPE allows to remove patient’s plasma from the blood and to replace it with fluids which do not contain the large substances, such as antibodies, targeted to be removed. It applies to a wide range of acute diseases but more rarely to chronic ones due to the adverse effects of the replacement fluids, human albumin or fresh frozen plasma, overtime.
DFPP
Cascade Filtration Double Filtration
in case of
Auto-immune diseases
Rejection of transplanted organs
Hypercholesterolemia
In case of acute diseases, cascade filtration/DFPP is usually performed as TPE with 5-10 consecutive sessions of 1-2 hours, while for chronic diseases it is performed a few times per year depending on the underlying disease and patient’s situation.
Like TPE, cascade filtration and DFPP allow to remove the larger substances from the blood, such as antibodies, fibrinogen or LDL-cholesterol. These substances could increase the blood viscosity. In this case, Double Filtration Plasmapheresis makes blood more fluid, the technique is also called rheopheresis.
The interest of cascade filtration/DFPP remains in the fact that the plasma is filtered and then returned to the patient, avoiding or minimizing the need for replacement fluids. Thus, it applies to both acute and chronic diseases as, in the contrary of TPE, it doesn't induce acute or long term immune reactions due to the injection of solutions of human origin such as albumin or fresh frozen plasma.
Technically speaking
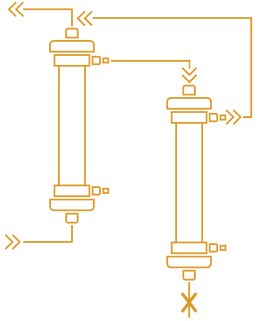
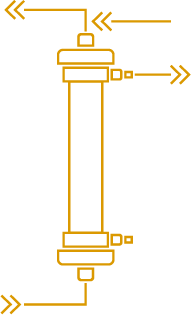
Cascade filtration is a 2 steps process during which plasma is first extracted from the blood and then circulated through a second filter named plasma fractionator having a pore size approximately 10 folds smaller than a plasmafilter, which retains the larger substances. While in cascade filtration the separation of plasma from blood can be obtained by centrifugation or filtration, in DFPP it is done by filtration only reason why the process can be named double filtration.
HP
Hemoperfusion
in case of
Ulcerative colitis
Crohn disease
Inflammatory Mediator Removal
Hemoperfusion can be used for both acute and chronic diseases, such as cascade filtration, and with the same frequency; 5 to 10 consecutive sessions of 1-2 hours.
Hemoperfusion can be used to directly remove specific substances from the blood by adsorption, a technique which fixes substances on a surface. It is of particular interest for leukocytes which are too big to be filtrated without major loss of red cells.
Technically speaking
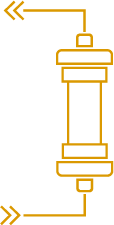
In hemoperfusion, blood is passed through a sorbent that retains the substances for which it is specifically designed. At the end of the treatment, the sorbent contains large amounts of this substance and is discarded. The sorbent directly interacts with the blood which is more prone to lead to some clinical side effects, such as bradykinine release, than plasma. Side effects and potential contraindications shall be pointed out by the manufacturer of such sorbent.
PP
PlasmaPerfusion
in case of
Auto-immune diseases
Rejection of transplanted organs
Hypercholesterolemia
Plasmaperfusion can be used for both acute and chronic diseases, such as cascade filtration, and with the same frequency; 5 to 10 consecutive sessions of 1-2 hours.
Plasmaperfusion allows to removes specific substances from the plasma by adsorption. It has on hemoperfusion the interest to lead to less side effects while compared to cascade filtration it is more specific for the targeted substances.
Technically speaking
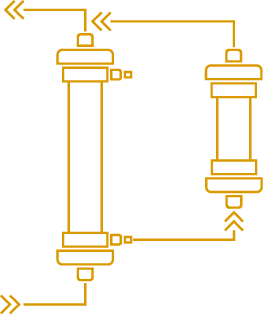
Plasmaperfusion is a 2 steps process during which plasma is first extracted from the blood and then circulated through a sorbent designed to retain some specific substances such as antibodies, Lp(a) or LDL cholesterol. The sorbent can be either single use and discarded at the end of the treatment or re-usable and regenerated after and/or during treatment.
A bit of
HISTORY
Plasmatherapeutic procedures have been performed for the first time at the beginning of the 20th century and their application becomes really active during the 70’s all over the world.
The first plasmapheresis was performed in Russia in 1913 by Yurevitch and Rosenberg to demonstrate the concept of “ … washing the blood outside the body …”. It consisted in extracting a portion of the rabbits blood which was then centrifuged to separate the red blood cells. These were then mixed to normal saline which was heated before being reinjected to the rabbits.
However the term plasmapheresis was defined by Pr John Abel in USA in 1914, combining two terms :
- Plasma: liquid part of the blood
- Aphaeresis: In Greek “removal
Thus, plasmapheresis was totally defined as a method of removal of plasma from an organism.
Unfortunately the First World War began which stopped the experiments and this technical approach was forgotten for a few decades.
In 1944, the Swedish physician Jan G. Waldenström described a case of Macroglobulinemia with symptoms of increased blood viscosity. In 1955, he performed effective plasmapheresis procedures on a patient with macroglobulinemia and noted an effective reduction of macroglobulin in the blood.
In 1963, several procedures were successfully performed on patients with Waldenström illness (Macroglobulinemia with high blood viscosity) which can be considered as the start of a regular application of plasmapheresis to a human disease.
Plasmapheresis is regularly performed in many countries since the 70’s with approximately 1000 procedures in England, 6200 in France and later in the 80’s with 50 000 procedures per year in the USA.
Today the term plasmapheresis includes different techniques (filtration or adsorption on plasma), which remove not all but only specific elements contained in the plasma, and altogether allow to treat a large number of diseases.
Hot topics

ERA 2025
Join us to the 62th European Renal Association (ERA) Congress in Vienna, Austria. ERA is based on 3 pillars: Education, Science and Networking. As Infomed, we support the association for around 20 years and we clearly appreciate to be a key partner to the association to develop excellence and quality of the scientific knowledge.

TRAINING SESSION
We offer several training sessions during the year, dedicated to all our partner. Book your place and become the reference of blood purification. The program is prepared to be accessible for everyone. Be carefull, place are limites, register early !

ASN
Come and share with us the Kidney Week organized by the American Society of Nephrology (ASN), in November in Houston, Texas. This key event is focus on education, training and knowledge sharing, through a large number of publications. Once again, we are pleased to support and take part by supporting the exchange of the international know-how in the field.