Home Dialysis
It is more flexibility and freedom for patients. Treatment is performed at home according to the patient’s schedule; it can be done during the evening, the night or whenever it is the most convenient.
The most common types of Home Dialysis are
PD
Peritoneal Dialysis
HD
HemoDialysis

Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis allows replacing the kidney function when it is not able to do the job adequately. The target is to remove waste products (toxins) from the patient’s body thanks to his own membrane, the peritoneum, which allows transfer of solutes and water to the peritoneal cavity from where it is extracted to a drain bag.
PD
Peritoneal Dialysis
in case of
Chronic renal failure
This therapy is usually performed daily with 4 to 5 exchanges either manually during the day (CAPD) or nightly with a machine (APD) for automatically refreshing the fluid.
In case of chronic renal failure, the peritoneal dialysis (PD) uses the patient's peritoneum as a membrane across which fluids and dissolved substances (electrolytes, urea, glucose, albumin and other small molecules) are exchanged beetween the blood and a fluid named dialysate which is injected in the abdomen.
Technically speaking
A fluid named dialysate is introduced through a permanent tube, the catheter, in the abdomen and flushed out after a dwell time of 1-3 hours which is the time necessary to transfer the waste products from the blood to the dialysate. It is done either every night while the patient sleeps (automatic peritoneal dialysis: APD) or via regular exchanges throughout the day (continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: CAPD).
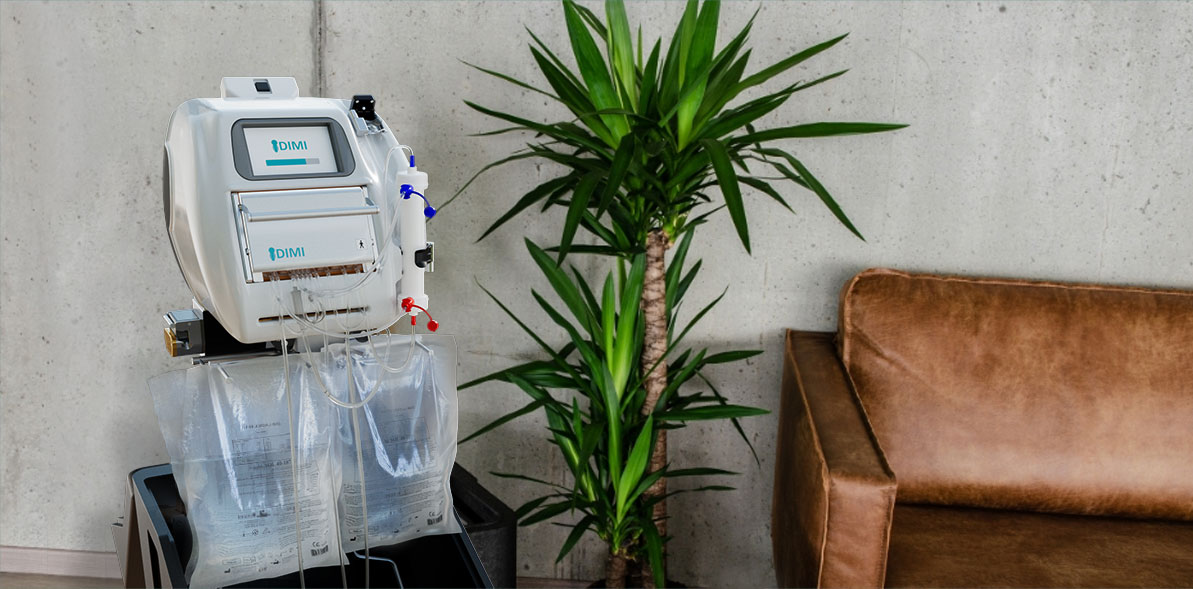
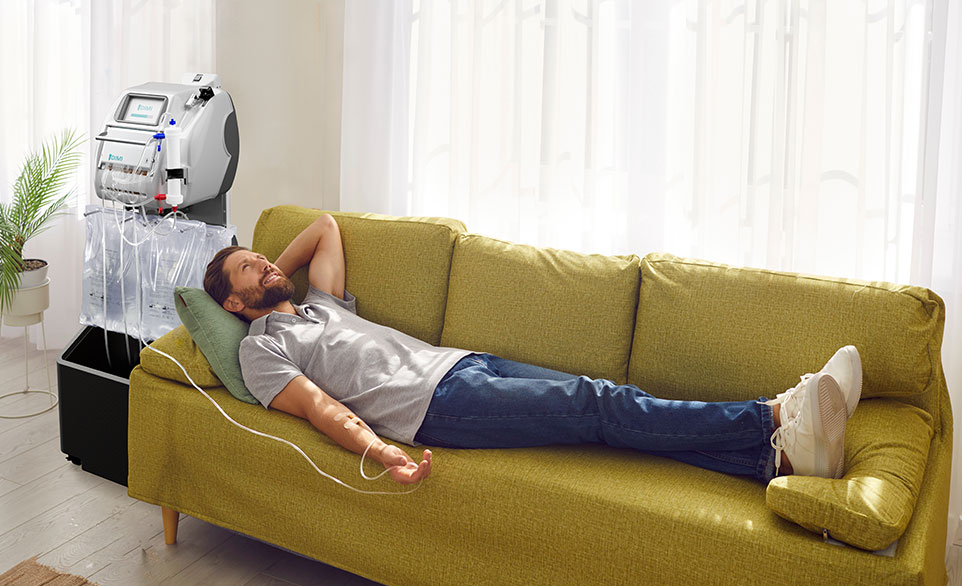
Home Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis can be performed at home. It is used in case of chronic kidney failure (CKD). Compared to in-center dialysis, home hemodialysis gives more freedom to the patient who can continue to work and keep an active lifestyle. Home hemodialysis is performed thanks to a machine that the patient manages with a schedule according to his availabilities.

HD
HemoDialysis
in case of
Chronic renal failure
This therapy is usually performed at least 3 times per week and up to 7 times during 2-8 hours according to the protocol which can be agreed upon between the doctor and the patient.
There are three main types of hemodialysis
- Conventional hemodialysis : is usually done three times per week, for 3–4 hours per each treatment.
- Daily hemodialysis : is usually done for 2-2.5 hours, six days per week
- Nocturnal hemodialysis : The procedure of nocturnal hemodialysis is similar to conventional hemodialysis excepted that it is performed three to six nights per week and between six and ten hours per treatment while the patient sleeps.
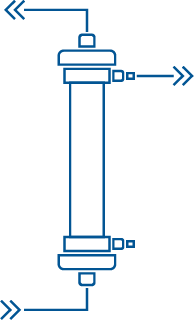
Technically speaking
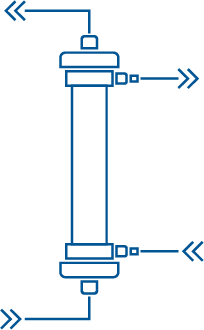
HDF
HemoDiaFiltration
in case of
Renal failure
This therapy is usually performed such as hemodialysis, at least 3 times per week and up to 7 times during 2-8 hours.
HDF is a combination of hemofiltration and hemodialysis which can be preferred to hemodialysis. Reasons for this are, for example, the higher clearance of medium size substances.
Technically speaking
In HDF, blood is passed through a hemo(dia)filter while dialysate is injected on the other side of the semi-permeable membrane at a rate which is less than that of the drain flow, which also includes ultrafiltrate, thus combining the filtration process to the dialysis one. In HDF, substitution fluid must be injected in the blood to compensate for the filtration flow.
UF
UltraFiltration
in case of
Fluid overload
UF is usually performed from 4 to 8 hours, until the targeted water volume to remove from the patient is reached.
UF is used to remove water from the body in case of fluid overload. Thus it allows to reduce the pressure within the body, especially on the heart, and to remove water that has cumulated within some organs, such as the lungs, and forms oedema there. At home, this therapy can be used alone or in addition to the others technics. In this latest case, the total volume of fluid injected is less than that removed from the patient, the difference providing the targeted removal of water.
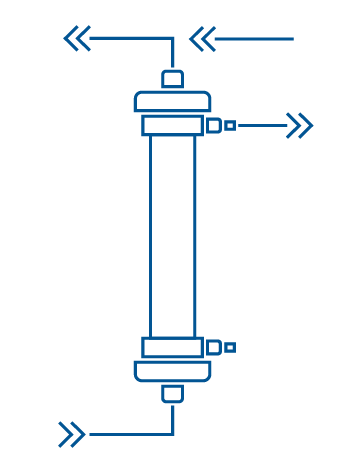
Technically speaking
In UF, blood is passed through a hemofilter which allows water to be filtrated, together with some other substances which are not of relevant importance in this case. The water is removed at a rate that is well tolerated by the patient and there is no compensation for the few undesired losses of other substances.
HHD advantages
Home Hemodialysis (HHD) offers several advantages; one of them is to let the patient set his own schedule. The patient can choose treatment times and duration with the medical team to fit other activities, such as going to work or caring for a family member.
Another advantage is the treatment quality as patients can dialyze more often at home. People who dialyze at a clinic skip 3 days each week (the interdialytic period) during which wastes and fluid buildup in their bodies. Dialyzing at home five to seven times per week means wastes and fluid don't build up as much in the body.
Patient’s pain is less present when HD is realized at home, in fact, muscle cramps that are common in people using the standard HD become less common in those who choose home HD because wastes and fluids are cleared more often.

Hot topics

ERA 2025
Join us to the 62th European Renal Association (ERA) Congress in Vienna, Austria. ERA is based on 3 pillars: Education, Science and Networking. As Infomed, we support the association for around 20 years and we clearly appreciate to be a key partner to the association to develop excellence and quality of the scientific knowledge.

TRAINING SESSION
We offer several training sessions during the year, dedicated to all our partner. Book your place and become the reference of blood purification. The program is prepared to be accessible for everyone. Be carefull, place are limites, register early !

ASN
Come and share with us the Kidney Week organized by the American Society of Nephrology (ASN), in November in Houston, Texas. This key event is focus on education, training and knowledge sharing, through a large number of publications. Once again, we are pleased to support and take part by supporting the exchange of the international know-how in the field.